Step 1:Instrument settings
False Color: Bright colors (false color) can improve contrast resolution by enhancing hard-to-discern soft tissue differences. Theoretically, the human eye can only discern a limited number of gray levels, but it can discern a greater number of levels of different colors. Therefore, changing the color can enhance the recognition of soft tissue structures. Pseudo-color does not change the displayed ultrasound information, but only improves the perception of the information.
2D image conditioning
The purpose of adjusting the two-dimensional image is to distinguish the myocardial tissue and the cardiac blood pool to the greatest extent while maintaining a high frame rate. The higher the frame rate, the smoother the image display and the more information you can get.
Parameters that affect frame rate
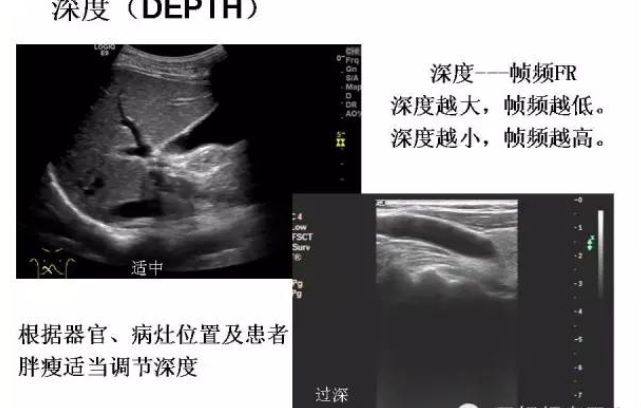
Depth: The depth image frame rate of the image. The greater the depth, the longer it takes for the signal to return to the probe, and the lower the frame rate.
Width: The larger the width of the image, the sparser the local sampling line density, and the lower the frame rate. Image zoom (zoom): The zoom function of the area of interest is of great value for the evaluation of relatively small structures and fast-moving structures, such as the morphology of valves.
Line density: The maximum scan line of each frame of image is the line density.
Two-dimensional image optimization method
Harmonic imaging (harmonics): Due to the strong side-lobe interference of the fundamental sound field and the relatively weak side-lobe interference of the harmonic sound field, the name of the sound image formed by using the human body information carried by the second harmonic in the echo (reflection or scattering) For ultrasound harmonic imaging.
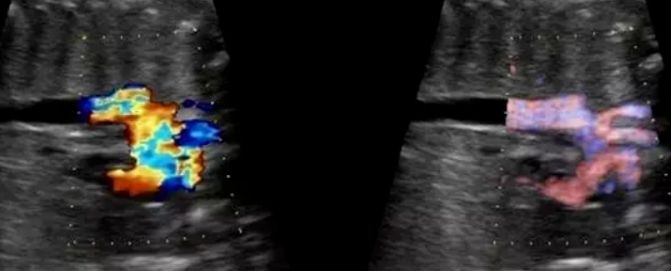
Multi-domain composite imaging (XBeam): Composite image processing in the frequency domain and spatial domain can effectively eliminate the adverse effects of spatial resolution reduction caused by image discretization and image attenuation, and make up for the lack of spatial resolution of the original image. Get a clearer image.
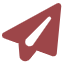
Step 2:Adjustment of color, power and high-resolution power Doppler
Because High-quality images mainly reflect
1. The image size is moderate
2. The image has appropriate light and shade
3. Good image contrast and high resolution
4. Good image uniformity
5. Increase color sensitivity and display low-speed blood flow
6. Reduce color spillover and remove aliasing
7. Increase the frame rate (capture high-speed blood flow signals)
8. Increase PW&CW sensitivity
Main menu settings
Gain control: If the color gain setting is too low, it will be difficult to display color signals. If the setting is too high, color spillover and aliasing will occur.
Wall filtering: Removes noise caused by blood vessel or heart wall motion. If the wall filter is set too low, colors will bleed through. If the wall filter setting is too high and the velocity range is adjusted too large, it will cause poor color blood flow display. In order to display low-speed blood flow, the speed range must be appropriately reduced to match the detected blood flow speed, so that the colored blood flow can be displayed optimally.
Sub menu settings
Color map: Each of the above color map display modes has options from low to high, using different colors to display different blood flow states.
Frequency: There are three options: high, medium and low. At high frequencies, the speed that can be measured is lower and the depth is shallower. At low frequencies, the speed that can be measured is higher and the depth is deeper. The medium frequency is somewhere in between.
Blood flow resolution (flowresolution): There are two options: high and low. Each option has several choices from low to high. If the blood flow resolution is set to low, the color pixels will be larger. When set to high, the color pixels are smaller.
Speed scale (scale): There are kHz, cm/sec, and m/sec options. Generally choose cm/sec. Balance: Control the color signals superimposed on the two-dimensional ultrasound image so that the color signals are only displayed within the blood vessel wall without spillage. The optional range is 1~225.
Smoothing: Smoothes colors to make the image look softer. Use two options, RISE and FALL, to achieve balance. Each option has several choices from low to high.
Line density: When line density increases, the frame rate decreases, but the information contained in color Doppler increases, and the boundaries between the cardiac blood pool, ventricular wall, and interventricular septum become clearer. When setting, you need to balance the relationship between line density and frequency, and try to achieve a higher line density at an acceptable frame rate.
Artifact suppression: Usually selected to be off.
Color baseline: Move the zero line of color Doppler up and down to eliminate or reduce color distortion so that color Doppler can more accurately reflect blood flow status.
Line filter: In order to achieve a balance between lateral resolution and image noise, you can select the number of lateral filters, with different options from low to high.\
Routine Ultrasound Adjustment---2D, CDFI, PW, etc.
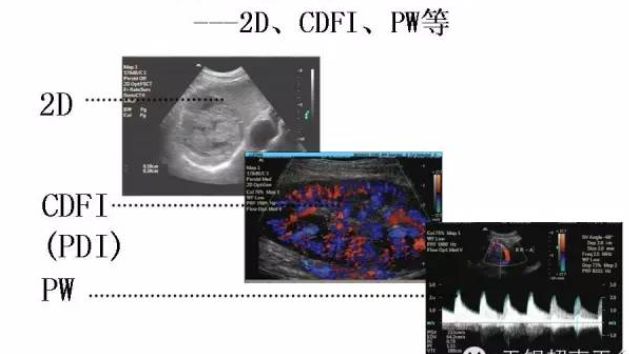
1.2D Adjustment

1.1 2D constant adjustment content
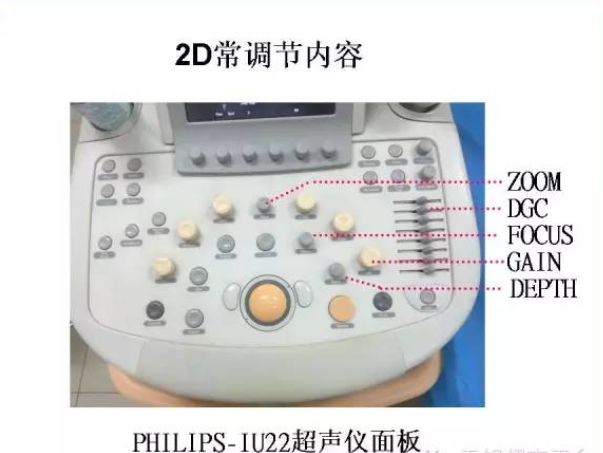
1.2
2D Non constant adjustment content


Depth:
Use low-frequency probes when superficial organ lesions are large
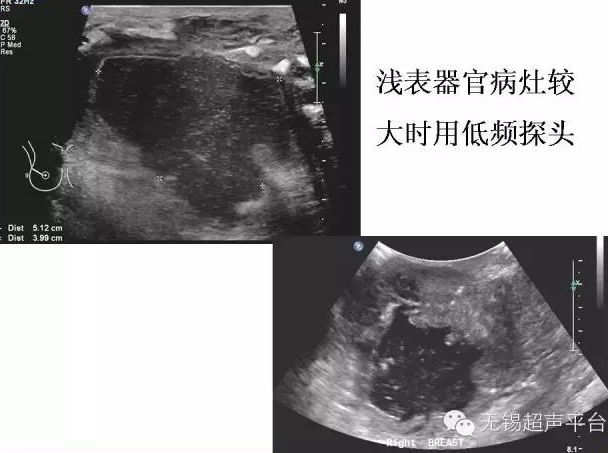
Image magnification function (read and write magnification) displays small structures and improves measurement accuracy
Image magnification function (read and write magnification) displays small structures and improves measurement accuracy
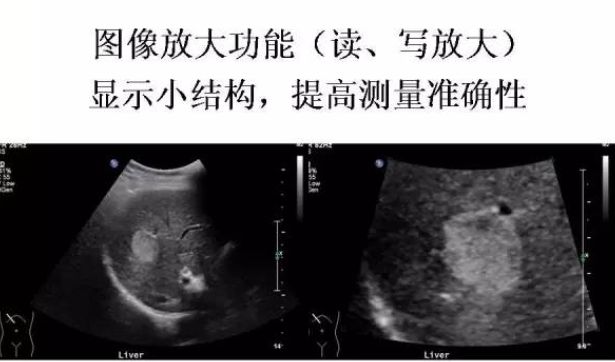
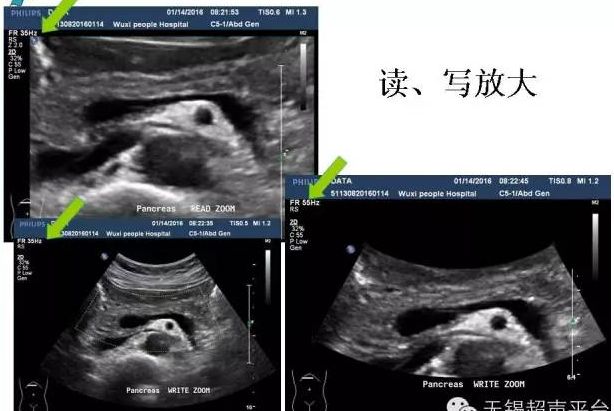
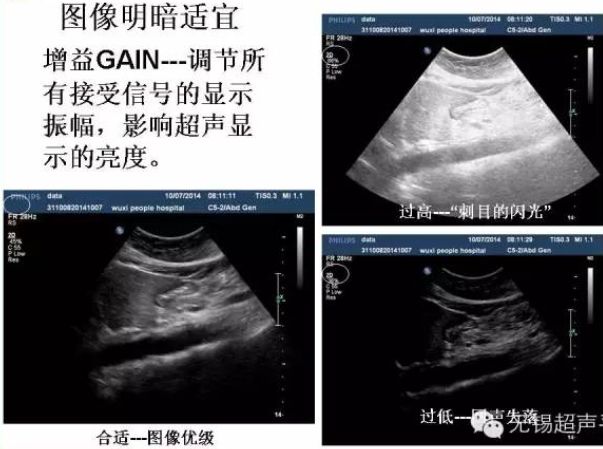
Image light and shade appropriate gain GAIN---adjusts the display amplitude of all received signals, affecting the brightness of the ultrasound display.
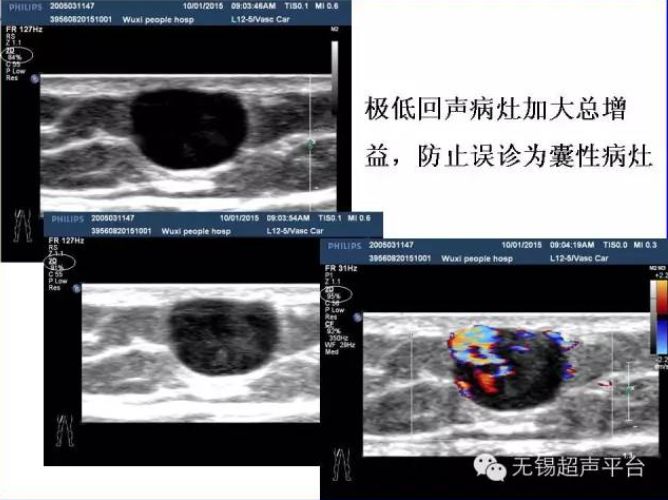
Extremely hypoechoic lesions increase the total gain to prevent misdiagnosis as cystic lesions
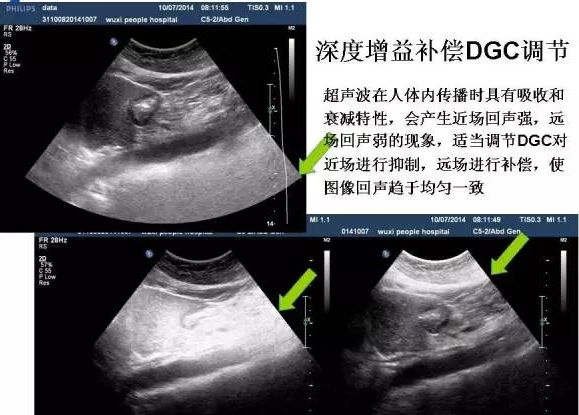
Depth gain compensation DGC adjusts the absorption and attenuation characteristics of ultrasonic waves when propagating in the human body, which will produce strong echoes in the near field and weak echoes in the far field. Appropriately adjust the DGC to suppress the near field and compensate for the far field, so that the image echo tends to Uniform
Post time: Nov-23-2023